Jaire Alexander joining the coin toss this past weekend might have cost him a big game.
Alexander was not named a game captain before the Green Bay Packers’ game in Carolina against the Panthers on Sunday, but the Charlotte native invited himself to the coin toss before the game.
Alexander called tails, and after winning the toss, he chose to play defense in the first half, not defer to the second half.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE SPORTS COVERAGE ON FOXNEWS.COM
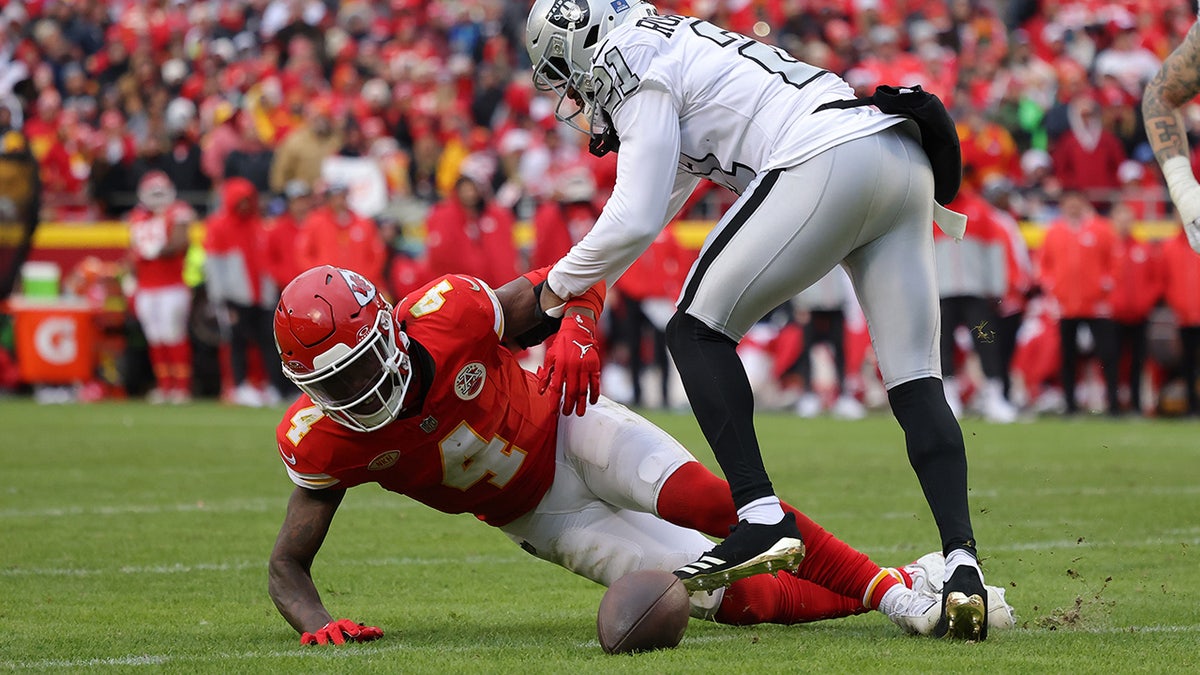
Green Bay Packers cornerback Jaire Alexander is shown in the fourth quarter against the Carolina Panthers, Dec. 24, 2023, at Bank of America Stadium in Charlotte, North Carolina. (Bob Donnan-USA TODAY Sports)
By choosing to play defense instead of deferring, the Panthers could have technically been allowed to receive the kickoff at the start of each half. The referee clarified the rule to Alexander, so issues were avoided at the time.
But the Packers announced Wednesday that they were suspending Alexander for one game due to “conduct detrimental to the team.”
“The decision to suspend a player is never easy and not one we take lightly. Unfortunately, Jaire’s actions prior to the game in Carolina led us to take this step,” general manager Brian Gutekunst said in a statement. “As an organization, we have an expectation that everyone puts the team first. While we are disappointed, we had a good conversation with Jaire this morning and fully expect him to learn from this as we move forward together. We look forward to welcoming him back next week as he is a valued member of this team and will continue to be in the future.”
Head coach Matt LaFleur called Alexander’s actions a “big mistake.”

The Green Bay Packers announced Wednesday that they were suspending Jaire Alexander for one game due to “conduct detrimental to the team.” (Kayla Wolf/Getty Images)
GIANTS DEMOTE TOMMY DEVITO TO BACKUP ROLE AFTER GETTING BENCHED ON CHRISTMAS
“That’s something that you review with the guys before they go out there every time about, ‘Hey, we win the toss, we’re going to defer,'” LaFleur said after the game, per ESPN. “I went to the officials before the game, made sure they knew what we were going to do. We had an incident earlier this year where we had a similar situation, so [we are] always trying to be proactive in that approach.”
Alexander didn’t even realize he had done anything wrong.
“I said, ‘I want our defense to be out there,’ and they all looked at me like I was crazy,” Alexander said. “I’m like, I mean, it’s pretty simple what I said, like I want the defense to be out there. They [were] like, ‘You mean defer?’ and I’m like, ‘Yeah, I guess.'”
Perhaps Alexander wanted a proper homecoming, but LaFleur made it seem like he had not been chosen as a captain for the game. It was also Alexander’s first game since Nov. 5 after dealing with a shoulder injury.
Alexander will be absent for the game on New Year’s Eve against the Minnesota Vikings, but he will return for the season finale when they host the Chicago Bears.

Jaire Alexander will be absent for the game on New Year’s Eve against the Minnesota Vikings, but he will return for the season finale when they host the Chicago Bears. (Stacy Revere/Getty Images)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
The Packers are currently the ninth seed in the NFC with a 7-8 record and a 26% chance to make the playoffs.
A loss this weekend would drop those chances to 1%, but a win bumps it up to 56%.
Follow Fox News Digital’s sports coverage on X and subscribe to the Fox News Sports Huddle newsletter.